Determination and Comparison of Corneal Endothelial Cell Changes in Phakic and Pseudophakic Patients Undergoing Vitrectomy with Silicone Oil Tamponade
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v42i1.2189
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v42i1.2189Abstract
Purpose: To determine and compare corneal endothelial cell changes between phakic and pseudophakic patients undergoing vitrectomy with silicone oil tamponade.
Study Design: Quasi experimental study.
Place and Duration of Study: Retina Eye Clinic, POB Eye Hospital,
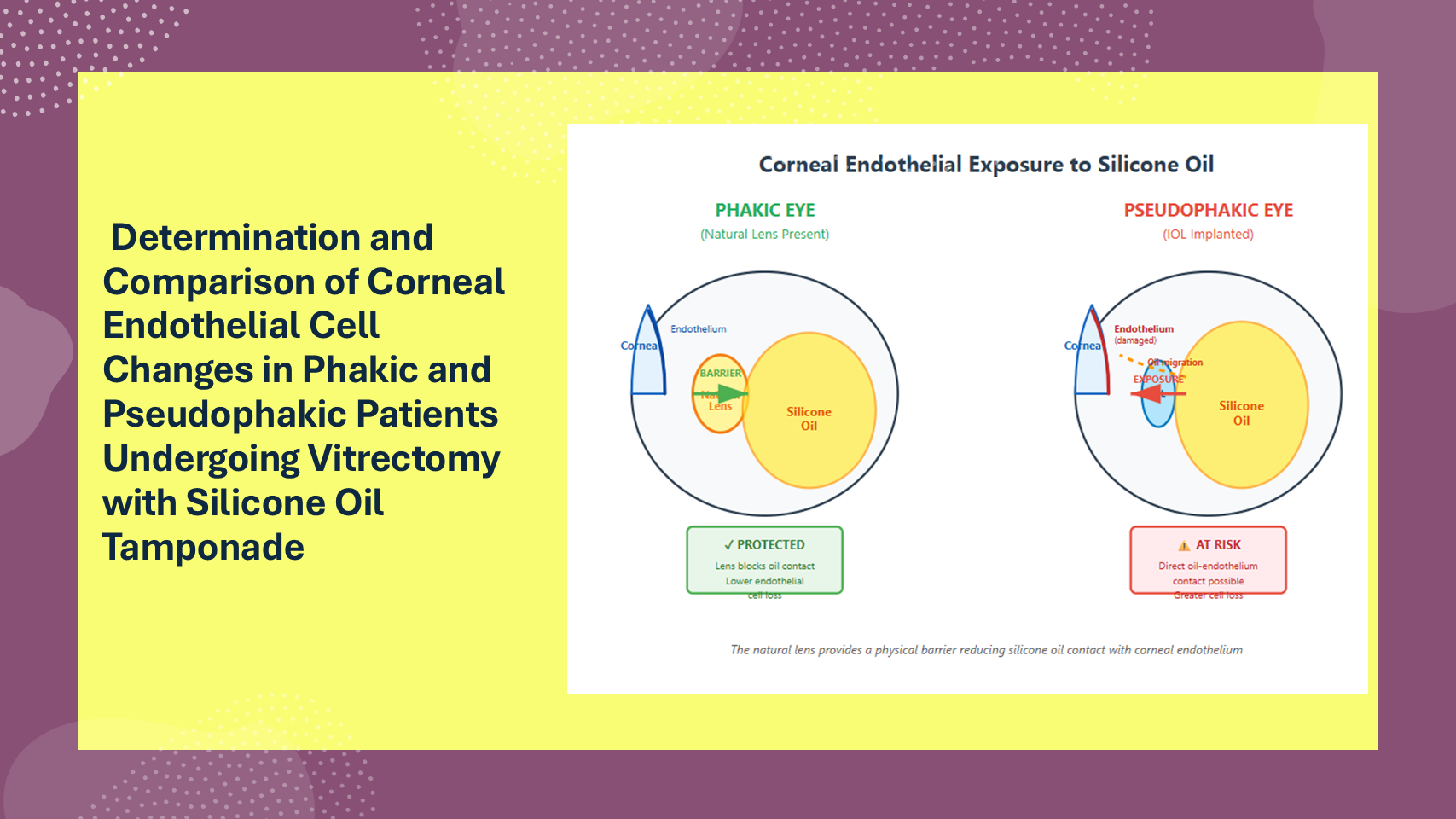
Methods: Fifty-six patients aged 18 to 65 years undergoing pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with silicone oil tamponade were included. They were divided into phakic and pseudophakic groups. Pars Plana Vitrectomy was done with 1000 centistoke silicone oil. Endothelial cell density (ECD) was measured using specular microscopy preoperatively and postoperatively on day 1, at 1 month, and at 3 months.
Results: The mean preoperative ECD was 2554.20 ± 127.36 cells/mm². On postoperative day 1, it decreased to 2495.25 ± 134.41 cells/mm², further declining to 2422.16 ± 141.22 cells/mm² at 1 month, and 2334.11 ± 152.09 cells/mm² at 3 months. Repeated measures ANOVA indicated a statistically significant effect of time on ECD (F (3,52) =1083.86, p<0.001), as well as a significant interaction between time and lens status (F (3,52) =61.23, p<0.001). Pseudophakic eyes exhibited a greater degree of endothelial cell loss compared to phakic eyes. Stratified analysis showed that age significantly influenced ECD loss, with older pseudophakic patients experiencing greater damage. Gender did not significantly modify the trend.
Conclusion: Pseudophakia is associated with greater endothelial damage. This highlights the importance of lens status in surgical planning and postoperative management, particularly in elderly patients.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Uzair Ahmed, Burhan Abdul Majid Khan, Faisal Murtaza, Muhammad Haseeb, Maryam Khalil

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






