Intra-Ocular Pressure after Injection of Intra-Vitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v42i1.2111
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v42i1.2111Abstract
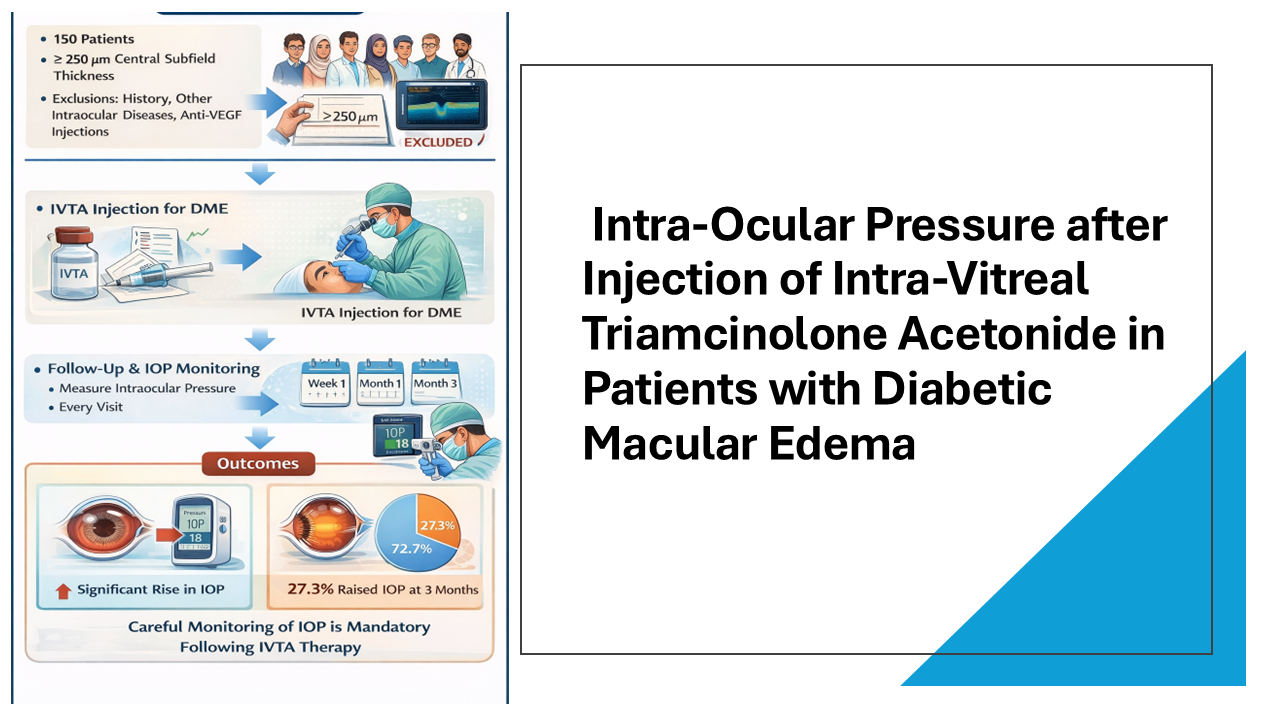
Purpose: To determine the frequency of raised intraocular pressure and the pattern of intraocular pressure changes following intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide (IVTA) injection in patients with diabetic macular edema(DME) for three months follow up.
Study Design: Quasi experimental study.
Place and Duration of Study: Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Center, Karachi from January 2024 to June 2024.
Methods: A total of 150 patients, scheduled for IVTA injection for DME with central subfield thickness of ≥ 250 µm were included. Patients with history any other intraocular diseases and previous retinal surgery or anti-VEGF injections were excluded. After IVTA injection, patients were followed up at week 1, month 1 and month. Pre-injection and post-injection intraocular pressure (IOP) were measured at each visit. Data analysis was performed using SPSS version 22.
Results: The median (IQR) age of participants was 36.0 (34-42) years. There were 70.0% males. The median duration since diagnosis of DME was 5.0 (3-5) months, and median HbA1c was 10.3 (9.6-11.2)%. The median baseline IOP was 17 (16-18) mmHg. Following IVTA injection, the median IOP was 18.0 (17-19) mmHg at 1 week, 19(17-20) mmHg at 1 month, and 18(18-22) mmHg at 3 months (p < 0.001). The frequency of raised IOP at 3 months post-injection was 41 patients (27.3%).
Conclusion: IVTA injection in patients with DME was associated with a significant rise in IOP, with 27.3% of patients developing raised IOP at 3 months. Careful monitoring of IOP is mandatory following IVTA therapy.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hadia yousuf

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






