Limbal Epithelial Stem Cell Transplantation for Ocular Chemical Burns: A Systematic Review
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v41i3.2029
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v41i3.2029Abstract
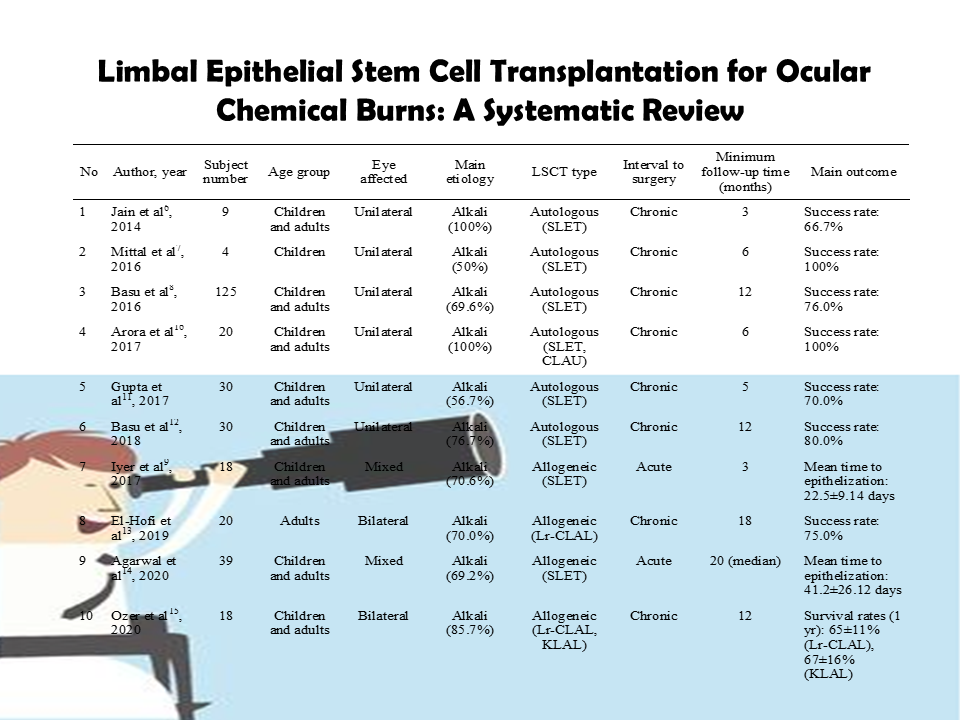
Ocular burns can cause limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD), which may require limbal stem cell transplantation (LSCT) to restore corneal function. This review evaluates outcomes of different LSCT techniques for treating ocular chemical injuries. A comprehensive search ofCochrane Library, PubMed, Scopus, EBSCO, and ProQuest, was conducted for studies published between 2014 and 2024, supplemented by manual searches. Studies focusing on LSCT for chemical injuries were included. The primary outcome was achievement of a stable, completely epithelialized, avascular corneal surface. Twelve studies, encompassing 473 eyes, met the inclusion criteria. Alkali injury was reported as the most common aetiology. The cumulative surgical success rates were 74.8% for autografts, 47.6% for allografts, and 54.4% for cultivated limbal epithelial transplantation. LSCT is a safe and effective intervention for ocular burns, particularly in severe LSCD cases, offering both anatomical restoration and functional visual improvement.
Keywords: Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency, Limbal Stem Cell Transplantation, Ocular Chemical Burns.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Andintia Aisyah Santoso, Muhammad Rheza Hilfaziyan Lubis, Mohammad Amin Rais Perfernandi Ilham

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






