Correlation of Intraocular Pressure with Intracranial Pressure in Patients undergoing lumbar puncture
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v41i3.1972
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v41i3.1972Abstract
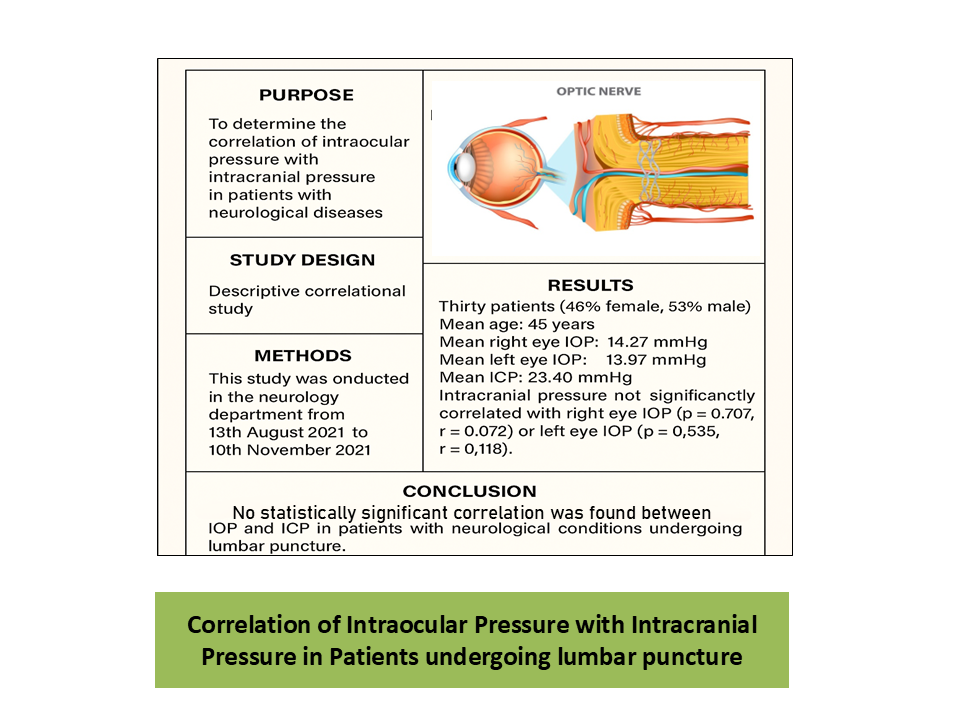
Purpose: To determine the correlation of Intraocular Pressure with Intracranial pressure in patients with neurological diseases.
Study Design: Descriptive correlational study.
Methods: This study was conducted in neurology department of Mayo Hospital, Lahore from 13th August 2021 to 10th November 2021, after receiving approval from ERB. Patients who never had any kind of intracranial surgery or spinal disease but endured lumber puncture because of different neurological symptoms were recruited by purposive sampling. Patients with glaucomatous nerve damage or any other disease affecting IOP, immune compromised and uncooperative patients were excluded. Intraocular pressure (IOP) of patients with raised Intracranial pressure (ICP), was measured using Applanation Tonometer. Data was entered in SPSS-23. Correlation analysis was evaluated by Pearson, while the p value <0.05 was considered significant.
Results: Thirty patients (n=30) including 46% females and 53% males fulfilled the inclusion criteria. The mean age of individuals was 45 years. The mean IOP of right eyes and left eyes were 14.27 ± 0.832 and 13.97± 0.786, respectively. Whereas the mean ICP was 23.40± 0.923. Intracranial pressure was neither significantly correlated with right eye IOP (p=0.707, r. =0.072), nor with the left eye (p=0.535, r=0.118,). However, a strong correlation was observed between OD-IOP and OS-IOP (r= .949, p= 0.00).
Conclusion: This study found no statistically significant correlation between IOP and ICP in patients with neurological conditions undergoing lumbar puncture. While a strong inter-eye correlation of IOP was noted, IOP measurements did not reliably reflect elevated ICP levels.
Keywords: Intraocular Pressure, Eye,Intracranial pressure, Glaucoma, Lumbar puncture.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dr. Rashida, Dr. Irfana , Dr. Samreen, Dr. Humera

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






