Thioridazine Induced Bilateral Angle Closure and Myopic Shift
Doi: 10.36351/pjo.v41i3.1960
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.36351/pjo.v41i3.1960Abstract
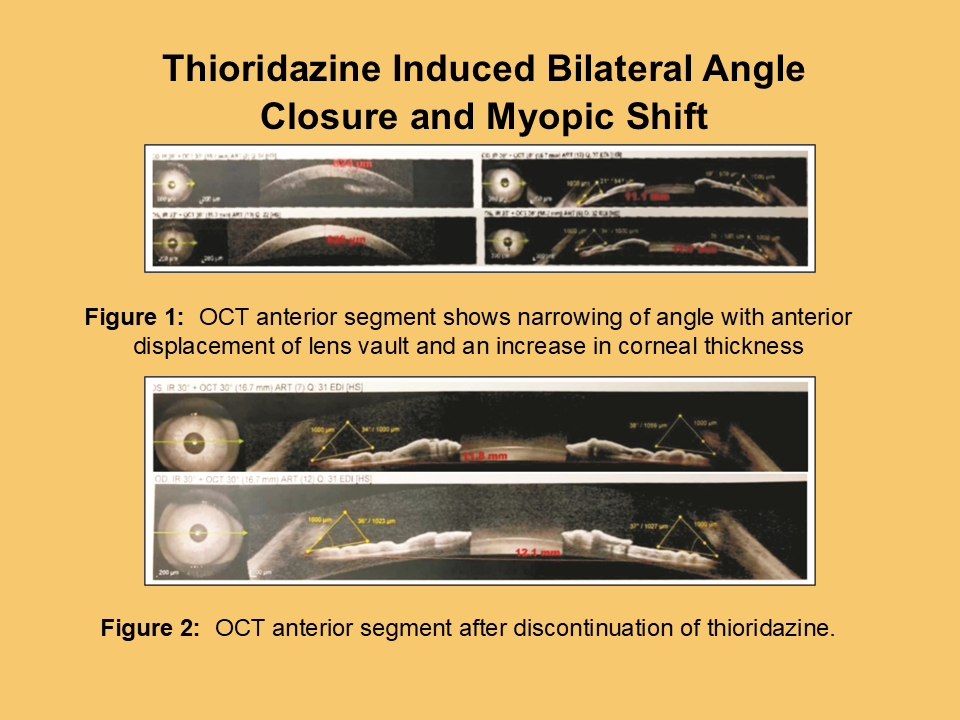
Drug induced angle closure is a sight threatening complication in ophthalmology which if not treated urgently can lead to perpetual vision loss. Identifying the cause of disease and timely intervention can prevent permanent damage to the eye. This case report presents a case and subsequent discussion on thioridazine induced angle closure along with transient myopia. Oral and topical pressure lowering drugs were prescribed which included oral acetazolamide 250mg QID, topical timolol, dorzolamide and brimonidine. This case report highlights some of the key issues pertaining to drug induce angle closure and the potential approach to tackling it.
Keywords: Thioridazine, Secondary Angle Closure, Myopia.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Laiba Tabassum, Aneeq Ullah Baig Mirza, Sohail Zia

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






